NATHSAGAR BADAL
NATHSAGAR
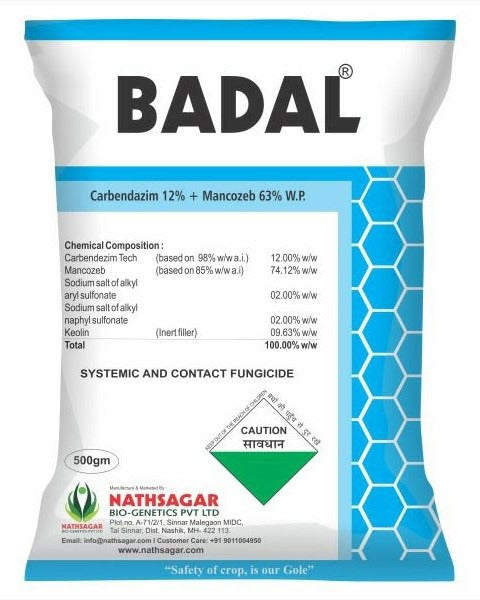
NATHSAGAR BADAL
NATHSAGAR
Price: ₹ 248
₹ 248
नियमित रूप से मूल्य
₹ 310
₹ 310
विक्रय कीमत
SKU: 250 gms
Currently Unavailable.
SKU: 250 gms
आप सहेजें: ₹ 62

Currently Unavailable.
/

- मूल देश: भारत
- सुरक्षित भुगतान
- भंडार में है भेजने के लिए तैयार
- रास्ते में सूची













